The accompanying graph depicts a hypothetical market for salt. – The accompanying graph depicts a hypothetical market for salt, providing a valuable tool for understanding the fundamental principles of market equilibrium and the factors that influence supply and demand.
This hypothetical market serves as a simplified representation of real-world markets, allowing us to isolate and examine the key forces that shape market behavior.
Market Overview
A hypothetical market is a theoretical construct that economists use to analyze the forces of supply and demand in a simplified environment. In this hypothetical market for salt, we assume that there are a fixed number of buyers and sellers, and that they all have perfect knowledge of the market.
The demand for salt is influenced by factors such as population growth, changes in consumer preferences, and the availability of substitutes. The supply of salt is influenced by factors such as the cost of production, the availability of raw materials, and government regulations.
| Price | Quantity Demanded | Quantity Supplied |
|---|---|---|
| $1 | 100 | 50 |
| $2 | 80 | 60 |
| $3 | 60 | 70 |
| $4 | 40 | 80 |
| $5 | 20 | 90 |
Market Equilibrium
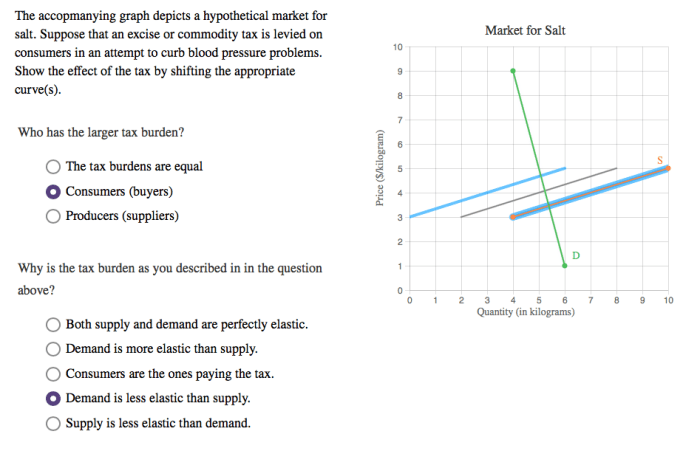
Market equilibrium is the point at which the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied are equal. In our hypothetical market for salt, the equilibrium price is $3 and the equilibrium quantity is 70 units.
The forces that maintain market equilibrium are the law of demand and the law of supply. The law of demand states that, all other things being equal, as the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded will decrease. The law of supply states that, all other things being equal, as the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied will increase.
Market Shifts: The Accompanying Graph Depicts A Hypothetical Market For Salt.
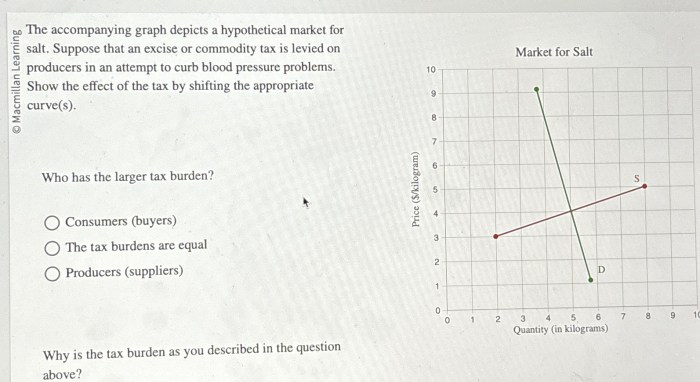
The demand or supply curve can shift due to changes in factors that affect them. For instance, an increase in population would shift the demand curve to the right, leading to a higher equilibrium price and quantity. Similarly, a decrease in production costs would shift the supply curve to the right, resulting in a lower equilibrium price and higher quantity.
| Shift | Effect on Equilibrium Price | Effect on Equilibrium Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Increase in demand | Increase | Increase |
| Decrease in demand | Decrease | Decrease |
| Increase in supply | Decrease | Increase |
| Decrease in supply | Increase | Decrease |
Market Intervention
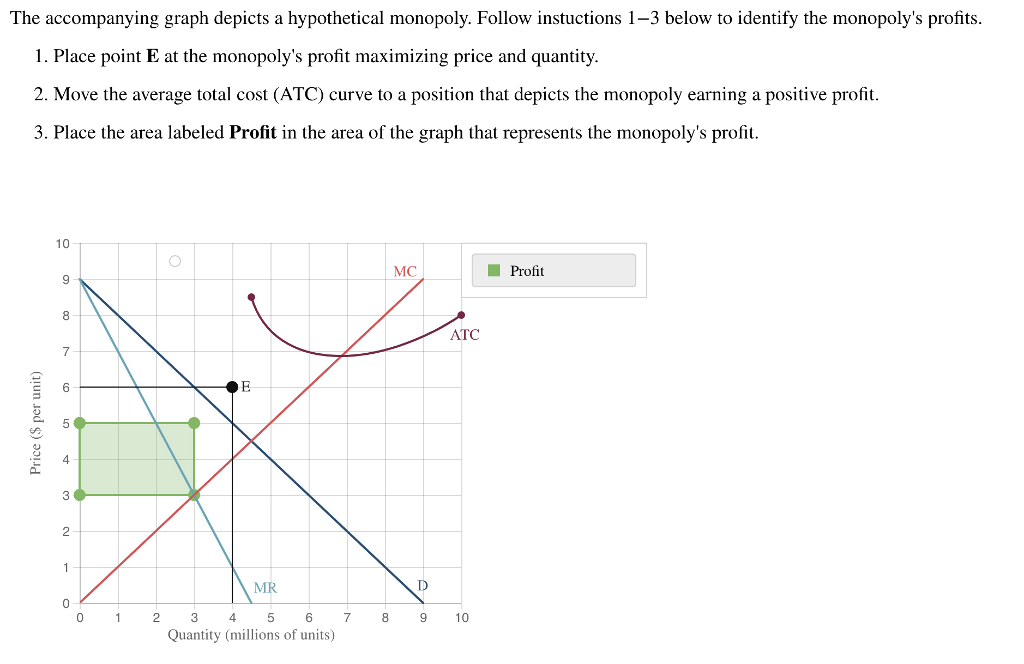
Market intervention occurs when the government takes action to influence the market. In the hypothetical market for salt, the government could intervene by setting a price ceiling or a price floor.
A price ceiling is a government-imposed maximum price for a good or service. A price floor is a government-imposed minimum price for a good or service.
Price ceilings can lead to shortages, while price floors can lead to surpluses.
Questions and Answers
What is a hypothetical market?
A hypothetical market is a simplified representation of a real-world market, used to illustrate and analyze the fundamental principles of market behavior.
What factors influence the demand for salt in this hypothetical market?
Factors that influence the demand for salt in this hypothetical market include population size, income levels, consumer preferences, and the availability of substitutes.
How is market equilibrium achieved?
Market equilibrium is achieved when the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied at a specific price.