Embark on an intriguing journey into the realm of point on a graph crosswords! This comprehensive guide will unravel the secrets of this captivating puzzle, providing you with the tools and insights to conquer any challenge that comes your way.
From understanding the fundamentals of points on a graph to mastering the art of plotting and analyzing data, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the world of point graphs with ease.
Understanding the Concept of Points on a Graph
A point on a graph is a single, specific location identified by its coordinates. The coordinate system is a framework that helps us locate points on a graph. It consists of two perpendicular lines, called the x-axis and y-axis, which intersect at a point called the origin.
The x-coordinate of a point tells us how far it is from the origin along the x-axis. The y-coordinate of a point tells us how far it is from the origin along the y-axis.
Types of Points on a Graph
There are different types of points on a graph, each with its own characteristics:
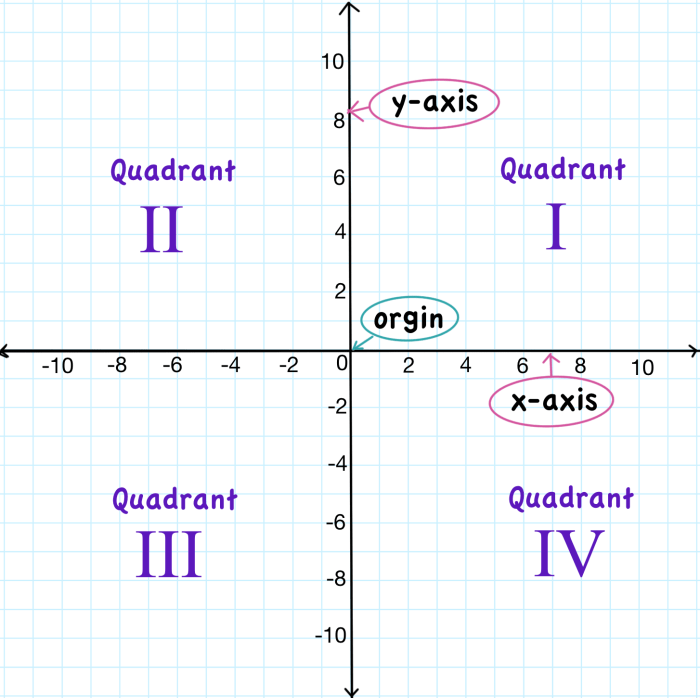
- Origin:The point where the x-axis and y-axis intersect is called the origin. Its coordinates are (0, 0).
- Quadrant:The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants by the x-axis and y-axis. Each quadrant is numbered I, II, III, or IV, starting from the top right and moving counterclockwise.
- Axis Points:Points that lie on either the x-axis or y-axis are called axis points. Their coordinates have either an x-coordinate of 0 or a y-coordinate of 0.
Plotting Points on a Graph
Plotting points on a graph is a fundamental skill in mathematics. It allows us to represent data visually and make inferences about the relationship between variables. To plot a point on a graph, we need to follow these steps:
- Identify the coordinate system.The most common coordinate system is the Cartesian coordinate system, which uses two perpendicular axes, the x-axis and the y-axis. The point where these axes intersect is called the origin.
- Locate the x-coordinate.The x-coordinate is the distance from the origin to the point along the x-axis. It is represented by the first number in the ordered pair that represents the point.
- Locate the y-coordinate.The y-coordinate is the distance from the origin to the point along the y-axis. It is represented by the second number in the ordered pair that represents the point.
- Plot the point.Once we have located the x- and y-coordinates, we can plot the point on the graph by placing a dot at the intersection of the two coordinates.
Accuracy and precision are crucial when plotting points on a graph. Inaccurate or imprecise plotting can lead to incorrect conclusions about the data.
Examples of Plotting Points Using Different Coordinate Systems
The Cartesian coordinate system is the most common coordinate system, but there are other coordinate systems that can be used for plotting points. Here are a few examples:
- Polar coordinate system:The polar coordinate system uses two coordinates, the radius and the angle, to represent a point. The radius is the distance from the origin to the point, and the angle is the angle between the positive x-axis and the line connecting the point to the origin.
- Spherical coordinate system:The spherical coordinate system uses three coordinates, the radius, the azimuthal angle, and the polar angle, to represent a point. The radius is the distance from the origin to the point, the azimuthal angle is the angle between the positive x-axis and the projection of the line connecting the point to the origin onto the xy-plane, and the polar angle is the angle between the positive z-axis and the line connecting the point to the origin.
- Cylindrical coordinate system:The cylindrical coordinate system uses three coordinates, the radius, the azimuthal angle, and the height, to represent a point. The radius is the distance from the origin to the point, the azimuthal angle is the angle between the positive x-axis and the projection of the line connecting the point to the origin onto the xy-plane, and the height is the distance from the xy-plane to the point.
The choice of coordinate system depends on the specific application.
Using Points on a Graph for Data Analysis

Points on a graph are powerful tools for data analysis, allowing us to visualize and interpret complex information. They provide a visual representation of data, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and relationships.
Graphs can plot various types of data, including numerical, categorical, and time-series data. Numerical data represents quantities, such as temperature, weight, or sales figures. Categorical data represents qualitative information, such as gender, occupation, or product categories. Time-series data represents data collected over time, such as daily stock prices or monthly sales figures.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
By plotting points on a graph, we can identify trends and patterns in the data. An upward trend indicates that the data is increasing over time, while a downward trend indicates a decrease. Linear trends represent a constant rate of change, while nonlinear trends represent a more complex relationship between the variables.
Patterns can also be identified by observing clusters or gaps in the data points. For example, a cluster of points in a certain region of the graph may indicate a specific relationship between the variables, while a gap may suggest a missing or outlier data point.
When solving a point on a graph crossword clue, one might consider the various colors of tang soo do belts , which range from white to black, representing different levels of skill and experience. Similarly, in a graph, points can represent different values or positions, and their location on the graph can convey important information.
Types of Graphs: Point On A Graph Crossword
Graphs are powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing data. Different types of graphs are used for different purposes, and each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Line Graphs
Line graphs are used to show how a variable changes over time. They are created by plotting points on a coordinate plane, and then connecting the points with lines. Line graphs are good for showing trends and patterns in data.
- Advantages:Easy to understand, can show trends and patterns, can be used to compare multiple data sets.
- Disadvantages:Can be difficult to see individual data points, can be misleading if the data is not evenly distributed.
Bar Graphs
Bar graphs are used to compare different categories of data. They are created by drawing bars that represent the values of each category. Bar graphs are good for showing the distribution of data and for comparing different groups.
- Advantages:Easy to understand, can be used to compare different categories of data, can be used to show the distribution of data.
- Disadvantages:Can be difficult to see individual data points, can be misleading if the data is not evenly distributed.
Pie Charts
Pie charts are used to show the proportions of different categories of data. They are created by dividing a circle into sectors, where each sector represents a category of data. Pie charts are good for showing the relative sizes of different categories.
- Advantages:Easy to understand, can be used to show the proportions of different categories of data, can be used to compare different data sets.
- Disadvantages:Can be difficult to see individual data points, can be misleading if the data is not evenly distributed.
Scatter Plots, Point on a graph crossword
Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two variables. They are created by plotting points on a coordinate plane, where each point represents a pair of data values. Scatter plots can be used to find correlations between variables and to identify outliers.
- Advantages:Can show the relationship between two variables, can be used to find correlations between variables, can be used to identify outliers.
- Disadvantages:Can be difficult to see individual data points, can be misleading if the data is not evenly distributed.
The type of graph that is best for a particular data set depends on the purpose of the graph and the nature of the data. It is important to choose the right type of graph to ensure that the data is presented in a clear and accurate way.
Applications of Point Graphs
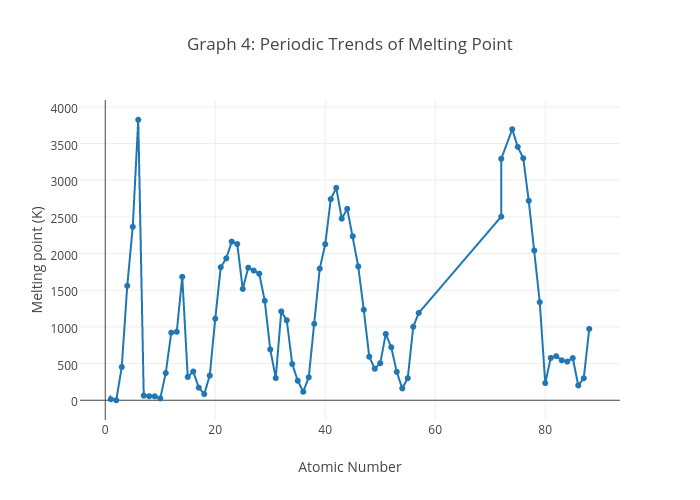
Point graphs are versatile tools used in various fields to visualize and analyze data. They provide a graphical representation of data points, enabling researchers, analysts, and professionals to identify trends, patterns, and relationships within datasets.
Let’s explore some key applications of point graphs:
Science
- In physics:Point graphs are used to plot the relationship between two variables, such as velocity and time, or force and displacement, to study motion and dynamics.
- In chemistry:Point graphs are used to represent the concentration of reactants and products over time, allowing for the analysis of chemical reactions and kinetics.
- In biology:Point graphs are used to visualize the growth patterns of organisms, the distribution of species, or the relationship between environmental factors and biological responses.
Engineering
- In mechanical engineering:Point graphs are used to plot stress-strain curves to analyze the mechanical properties of materials.
- In electrical engineering:Point graphs are used to represent the relationship between voltage and current in electrical circuits.
- In civil engineering:Point graphs are used to plot load-deflection curves for structural analysis and design.
Economics
- In microeconomics:Point graphs are used to represent supply and demand curves, elasticity, and consumer preferences.
- In macroeconomics:Point graphs are used to plot economic indicators such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment rates over time.
- In econometrics:Point graphs are used to visualize the relationship between economic variables and to test hypotheses.
Other Applications
- In sports analytics:Point graphs are used to track player performance, analyze team dynamics, and predict outcomes.
- In healthcare:Point graphs are used to visualize patient data, track disease progression, and monitor treatment outcomes.
- In data visualization:Point graphs are commonly used in dashboards and reports to present data in a clear and concise manner.
General Inquiries
What is a point on a graph?
A point on a graph is a specific location defined by its coordinates, which indicate its position on the x and y axes.
How do I plot a point on a graph?
To plot a point on a graph, locate its x-coordinate on the horizontal axis and its y-coordinate on the vertical axis. Mark the intersection of these two lines to represent the point.
What are the different types of graphs?
Common types of graphs include line graphs, bar graphs, scatter plots, and pie charts, each with its own advantages and uses for data visualization.